The Ultimate Guide to Jenkins Deployment Using Docker Compose
Introduction
Jenkins is a powerful automation tool widely used for continuous integration and deployment. Setting up Jenkins in a production environment can be challenging, but with Docker Compose, you can simplify the deployment process while ensuring a secure and efficient configuration. This guide also includes setting up Jenkins Agents for distributed builds using Docker Compose.
Docker Compose File for Jenkins and Jenkins Agent
Here is the Docker Compose file used to deploy Jenkins Master and Jenkins Agent:
services:
jenkins-master:
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
container_name: jenkins
restart: unless-stopped
user: 1000:1000 # Explicit user ID mapping
ports:
- "8080:8080"
- "50000:50000"
volumes:
- jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home:rw
environment:
- JAVA_OPTS=-Dhudson.security.csrf.GlobalCrumbIssuerStrategy=true -Djenkins.security.SystemReadPermission=true
networks:
- jenkins_network
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
read_only: true # Use a read-only filesystem
tmpfs:
- /tmp:size=2G # Use tmpfs for temporary storage
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "curl -f http://localhost:8080/login || exit 1"]
interval: 1m30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: '2'
memory: 2G
reservations:
cpus: '1'
memory: 1G
jenkins-agent:
image: jenkins/ssh-agent
container_name: jenkins-agent
restart: unless-stopped
expose:
- "22"
volumes:
- jenkins_agent:/home/jenkins/agent:rw
- type: bind
source: ./jenkins_agent_keys
target: /home/jenkins/.ssh
read_only: true
environment:
- SSH_PUBLIC_KEY_DIR=/home/jenkins/.ssh
networks:
- jenkins_network
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
tmpfs:
- /tmp:size=2G # Use tmpfs for temporary storage
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: '1'
memory: 1G
reservations:
cpus: '0.5'
memory: 512M
networks:
jenkins_network:
driver: bridge
volumes:
jenkins_home:
driver: local
jenkins_agent:
driver: localAdvantages of This Setup
- Simplified Deployment:
- Using Docker Compose streamlines the deployment process, making it easy to manage Jenkins and its agents.
- Agent Integration:
- Automatically sets up Jenkins Agents to distribute builds across multiple nodes, increasing scalability.
- Security Best Practices:
- Read-only file systems and restricted privileges (
no-new-privileges) enhance security. - CSRF protection (
GlobalCrumbIssuerStrategy) and system read permissions ensure a secure environment.
- Read-only file systems and restricted privileges (
- Resource Management:
- Defined resource limits and reservations prevent resource contention in production.
- Efficient Storage Management:
- Volumes ensure persistence for Jenkins data.
- Temporary storage with
tmpfsavoids unnecessary disk I/O.
- Health Monitoring:
- A health check ensures the Jenkins master container is running as expected.
Importance of Main Components
1. Jenkins Master
The jenkins-master service is the central component, responsible for orchestrating builds and managing jobs. Key configurations include:
- Volumes: Ensure Jenkins data persists across container restarts.
- Health Check: Monitors the service’s availability.
- Resource Limits: Prevents overutilization of system resources.
2. Jenkins Agent
The jenkins-agent service provides scalable build execution. Key configurations include:
- Bind Mount for SSH Keys: Securely connects the agent to the master.
- Exposed Port: Allows the master to communicate with the agent over SSH.
3. Volumes
jenkins_home:Stores all Jenkins configurations, jobs, and plugins persistently.jenkins_agent:Maintains the workspace and data for builds.- Bind Mount for SSH Keys: Ensures secure agent communication.
Use the following script to create the required folders and set permissions:
Startup Script for Manual Setup
Use the following script to create the required folders and set permissions:
#!/bin/bash
# Exit script on error
set -e
echo "Preparing environment for Jenkins deployment..."
# Define SSH keys directory
JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR="./jenkins_agent_keys"
# Create SSH keys directory
echo "Creating SSH keys directory for Jenkins Agent..."
mkdir -p "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR"
# Generate SSH keys for Jenkins Agent
echo "Generating SSH keys for Jenkins Agent..."
if [ ! -f "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/id_rsa" ]; then
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/id_rsa" -N ""
chmod 600 "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/id_rsa"
chmod 644 "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/id_rsa.pub"
else
echo "SSH keys already exist. Skipping key generation."
fi
# Copy public key to authorized_keys
echo "Configuring authorized_keys for Jenkins Agent..."
cp "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/id_rsa.pub" "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/authorized_keys"
chmod 644 "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR/authorized_keys"
# Set permissions for SSH keys directory
chmod -R 700 "$JENKINS_AGENT_KEYS_DIR"
# Ensure everything is ready
echo "Environment setup is complete!"
echo "You can now run 'docker-compose up -d' to start Jenkins."1.Prepare the Host Machine
- Ensure Docker and Docker Compose are installed on your machine.
- Check for sufficient disk space and memory (at least 2GB RAM and 10GB free disk space).
2.Create Required Directories
- Run the
setup.shscript provided to create the necessary directories and generate SSH keys for agent communication.
./setup.sh

3.Set Permissions
- The
setup.shscript will automatically set the required permissions for thejenkins_agent_keysdirectory. - Verify permissions by running:
ls -ld ./jenkins_agent_keys

4.Start Jenkins Services
- Run the following command to start the Jenkins master and agent containers:
docker-compose up -d
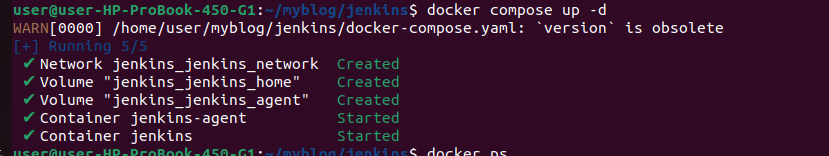
5.Check containers status
Run the following command to check containers are running or not
docker ps
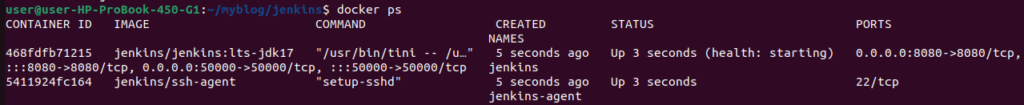
Since the Jenkins master is initializing, it will take some time to show a healthy status.
Check after 1 or 2 minutes ,you can see both master& agent containers are up & healthy

6.Access Jenkins
Open your web browser and navigate to http://<your-server-ip>:8080 to access the Jenkins web interface.Follow the setup wizard to configure Jenkins.

To retrieve the initial admin password for login run the below command
docker exec -it jenkins cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword

After giving password jenkins will prompt to install the suggested plugins.Do that

Once it finished will ask for configure admin password.Click save & continue

Since we are doing this on the local system for now, let it remain the same URL. In the upcoming section, we will point this to a domain name.
Once you completed we can see the jenkins dashboard as below
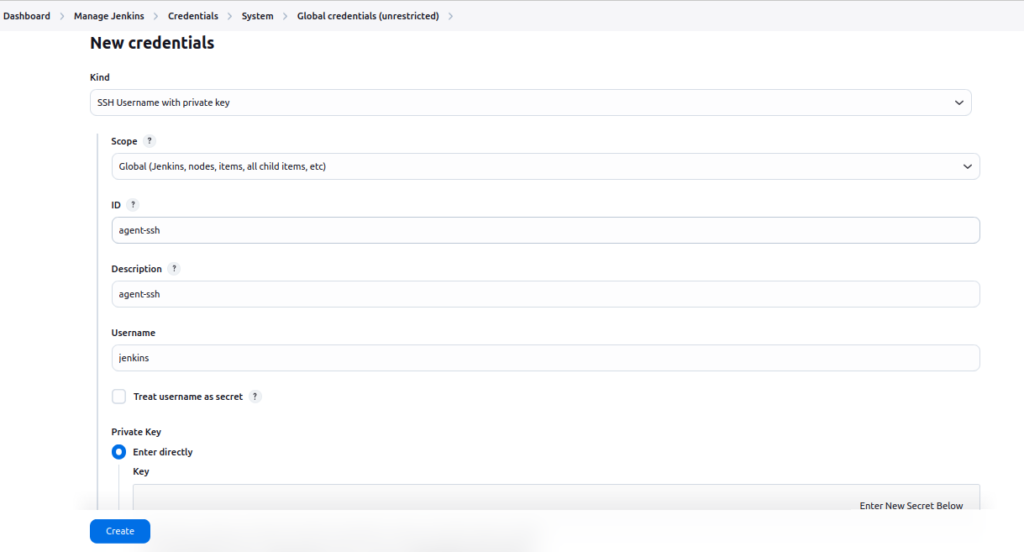
Configure SSH Credentials in Jenkins
- Add the private key (
id_rsa) from thejenkins_agent_keysfolder as a credential in Jenkins. - Navigate to Manage Jenkins > Manage Credentials and add a new SSH key.
Verify Agent Connection
Go to Manage Jenkins:
- From the dashboard, click Manage Jenkins.
- Then, click Manage Nodes and Clouds.
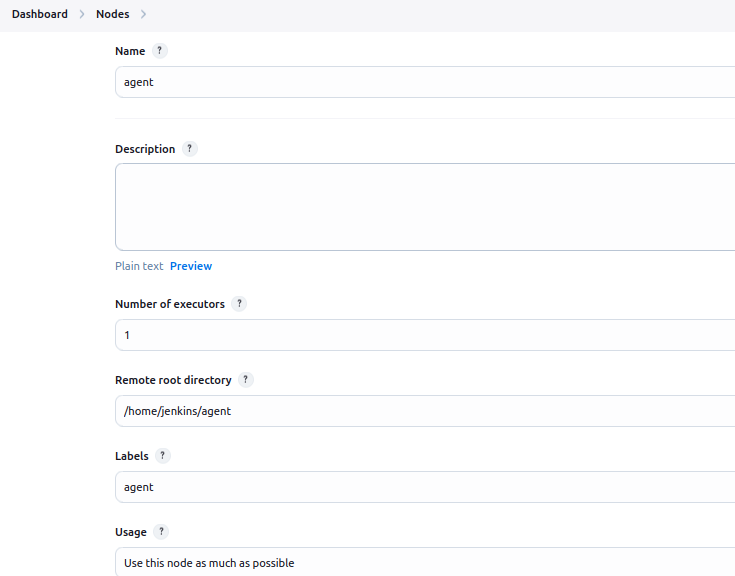
Add a New Node:
- Click on New Node.
- Enter a name for your node, such as
agent. - Select Permanent Agent, and click OK.

Configure the Node:
- Remote Root Directory: Set this to
/home/jenkins/agent(the volume mounted for the agent container). - Labels: Add appropriate labels like
agentfor categorizing the node. - Launch Method:
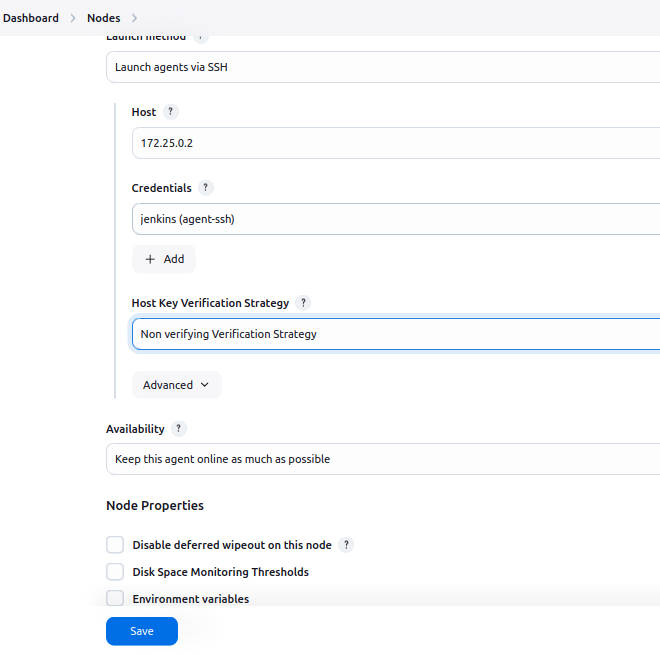
- Select Launch agent via SSH.
- Fill in the following:
- Host: Enter the IP address of the agent container (will get from docker inspect jenkins-agent).
- Command used to get container ip: docker inspect -f ‘{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}’ jenkins-agent
- Credentials:
- Click Add, and select Jenkins.
- Choose SSH Username with Private Key.
- Enter
jenkinsas the username. - Paste the private key (
id_rsa) contents into the key field.
- Host Key Verification Strategy:
- Select Non-verifying Verification Strategy for simplicity. For production, consider verifying host keys.
- Credentials:
Save the Node Configuration: Click Save to complete the configuration
Verify Connection:
- Jenkins will attempt to connect to the agent. If successful, the agent’s status will show as Connected.

You can just ignore the free swap & temp space warnings.That can be configured later also
Test the CI/CD Pipeline
- Create a simple freestyle or pipeline job to ensure the agent can execute builds.
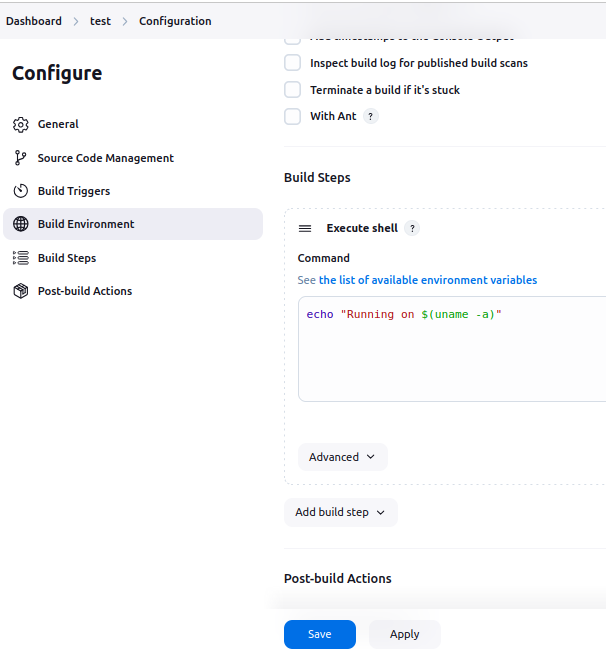
- Use a basic script like:
echo "Running on $(uname -a)"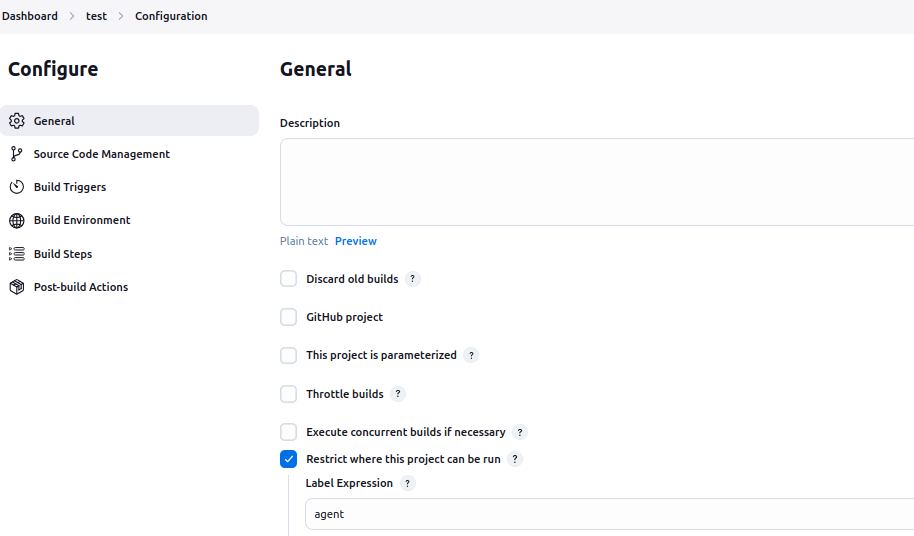
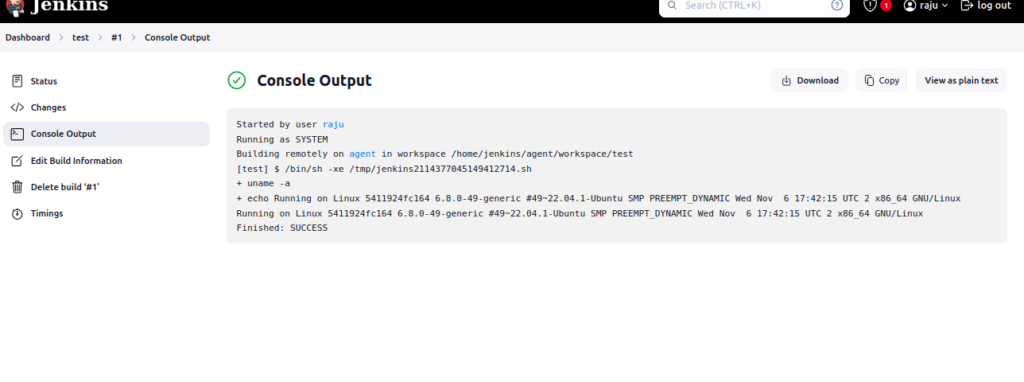
You can find the used code directly from the repo: https://github.com/rjshk013/cldop-blog/tree/main/jenkins/jenkins-01
Also you can clone the repo https://github.com/rjshk013/cldop-blog/ and navigate to directory
jenkins/jenkins-01 to find the files
Conclusion
This Docker Compose setup for Jenkins provides a secure, efficient, and scalable solution for production use. By following best practices, such as using Docker volumes, enabling health checks, and securing communication between the master and agent, you can ensure a robust CI/CD pipeline.
Deploy Jenkins using this setup to streamline your development workflows and enhance productivity.